Passive CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a technology that allows multiple different data signals to be sent simultaneously over a single optical fiber by using different colors (wavelengths) of light. The term "passive" means the system uses no electrical power—it relies on simple optical components to combine, separate, and manage these light signals.
Key Components & How It Works
Imagine a single fiber as a highway. Passive CWDM creates multiple non-interfering lanes on this highway, each lane being a specific wavelength of light.
Transmitters
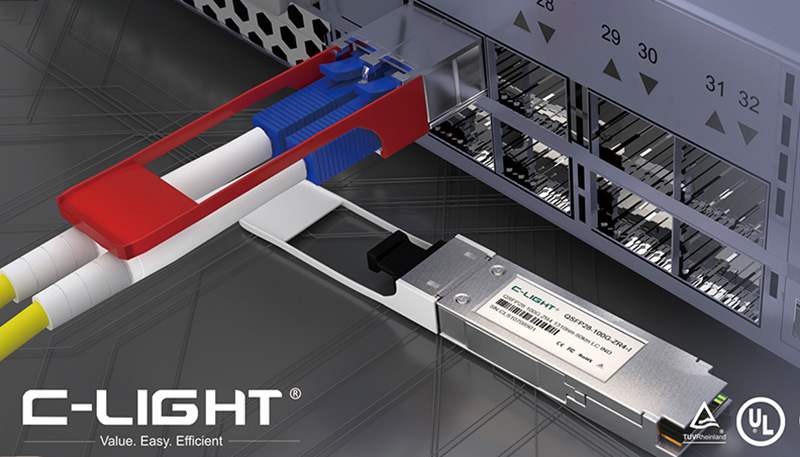
At the starting end, you have separate optical transceivers (e.g., in switches or routers). Each emits a laser signal at a **specific, standardized CWDM wavelength (e.g., 1270nm, 1290nm, 1310nm... up to 1610nm).
Multiplexer (Mux)
This is a passive, unpowered device. It acts like a combiner or funnel. It takes all the different colored light signals from the multiple transceivers and merges them onto a single outgoing fiber.
The Fiber
The single fiber now carries all the combined wavelengths over long distances (typically up to 80 km, depending on optics).
Demultiplexer (Demux)
At the receiving end, another passive device acts as a color filter or prism. It separates the combined light back into its individual wavelengths.
Receivers
Each separated wavelength is directed to its corresponding optical receiver, which understands only that specific color.
Why is it Coarse?
The wavelength channels in CWDM are spaced 20 nanometers (nm) apart (e.g., 1270, 1290, 1310 nm...). This wide spacing is coarse compared to Dense WDM (DWDM), where channels are spaced 0.8 nm or even 0.4 nm apart.
Advantage of Coarse Spacing:Much cheaper components (lasers, filters). The lasers don't need to be as thermally stable.
Trade-off:Fewer total channels. The standard CWDM grid defines 18 channels but in practice, 8 channels (1470nm to 1610nm) are most commonly used because of fiber attenuation characteristics.
Why is it Passive?
The key devices—the Multiplexer and Demultiplexer—are based on passive optical filter technology (like thin-film filters). They:
●Require no electrical power.
●Have no active electronics to process or amplify the signal.
●Are highly reliable and have a long operational life.
●Introduce very low insertion loss.
 TEL:+86 158 1857 3751
TEL:+86 158 1857 3751 

























































 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>



