
Cisco is riding a new wave of growth in AI hyperscale infrastructure, where bandwidth demands require massive capacity to handle expansion both inside and across data centers.
In the first quarter of fiscal 2026, AI infrastructure orders from hyperscale customers reached $1.3 billion. This includes Cisco’s unified programmable network architecture, the Silicon One system, as well as its optics portfolio.
Cisco’s strength in advanced AI use cases is evident. The company projects that AI infrastructure revenue from hyperscale customers will reach approximately $3 billion in fiscal 2026. In terms of orders, the volume expected from these same customers this year is at least double that of fiscal 2025.
Scale‑up and Cross‑Data Center Interconnect Opportunities
Within the hyperscale sector, Cisco sees an opportunity to strengthen its position in the data center interconnect scale‑up and scale‑out segments through its pluggable optics and latest terabit‑class router series.
Scale‑up involves increasing a data center’s capacity or performance by adding more resources to an individual server or system, such as upgrading components within a single physical or virtual server—like adding more powerful CPUs or processor cores and increasing memory.
Scale‑out has emerged as a new networking paradigm in AI, extending high‑performance computing beyond a single data center to connect multiple geographically distributed infrastructures into a unified “AI factory.”
As hyperscale customers look to expand AI clusters across their infrastructure to accommodate both scale‑up and scale‑out needs, demand is growing for Acacia coherent pluggable optics, which offer cost and power savings.
Similarly, Cisco is gaining momentum in its terabit‑class networking equipment, centered on the Silicon One P200 chip. This chip delivers 51.2 Tbps throughput for demanding AI/ML data center networks, supporting the scale‑out architecture that connects distributed AI clusters. The flagship product is the Cisco 8223 router—a compact (3RU) system with sixty‑four 800G ports designed to serve as the backbone for large‑scale AI training.
This 51.2‑terabit fixed Ethernet routing system is built for dense AI workload traffic between data centers. With Silicon One’s unparalleled scalability, power efficiency, and programmability, it delivers performance and speed across data centers that previously could only be achieved with intra‑data center switching infrastructure.
Although Silicon One continues to grow—Cisco expects to ship its one‑millionth chip in the second quarter of fiscal 2026—product orders for AI use cases beyond hyperscale customer training are also rising. This quarter, data center systems orders for inference and agent‑workflow networking saw double‑digit growth.
Networking Business Leads Revenue Mix
Driven by growth in its networking segment, Cisco’s total revenue for the quarter reached $14.9 billion, up 8% year over year. This performance was supported by strong demand for AI infrastructure and campus networking solutions.
With the overall networking portfolio growing 15%, Cisco highlighted outstanding performance in networking, where service provider routing delivered strong high‑single‑digit growth, largely driven by AI infrastructure revenue. Service provider and cloud product orders remained robust, rising 45% year over year, fueled by double‑digit growth from hyperscale customers. Demand from telecommunications customers was also strong in Q1, with orders up more than 25% year over year.
Cisco’s product revenue totaled $11.1 billion for the quarter, a 10% increase year over year, while services revenue reached $3.8 billion, up 2%. Data center switching and enterprise routing also contributed double‑digit growth, while campus switching posted high‑single‑digit growth.
However, the security business declined 2%. According to Patterson, the decline “reflects the downturn of legacy products and our transition of the Splunk business to cloud subscriptions, partially offset by growth in Secure Firewall, Duo, and SASE.” Similarly, collaboration fell 3%, reflecting decreases in devices and WebEx; observability grew 6%, led primarily by ThousandEyes growth.
Looking ahead to the second fiscal quarter, Cisco expects revenue in the range of $15.0 billion to $15.2 billion. For the full fiscal year 2026, Cisco projects revenue between $60.2 billion and $61.0 billion.
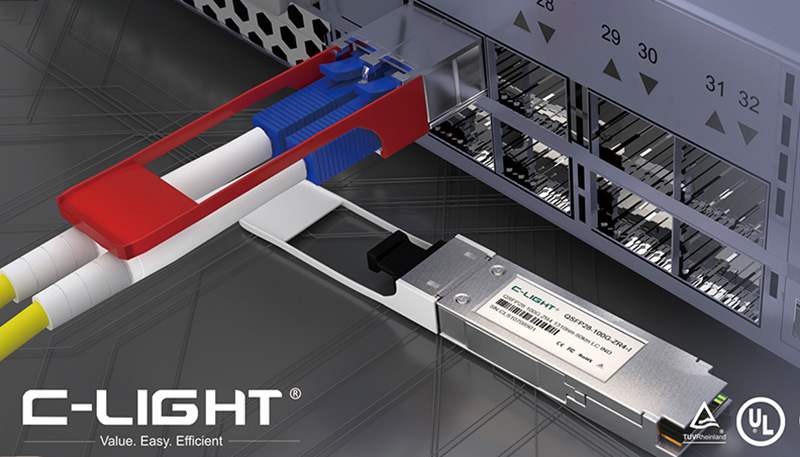
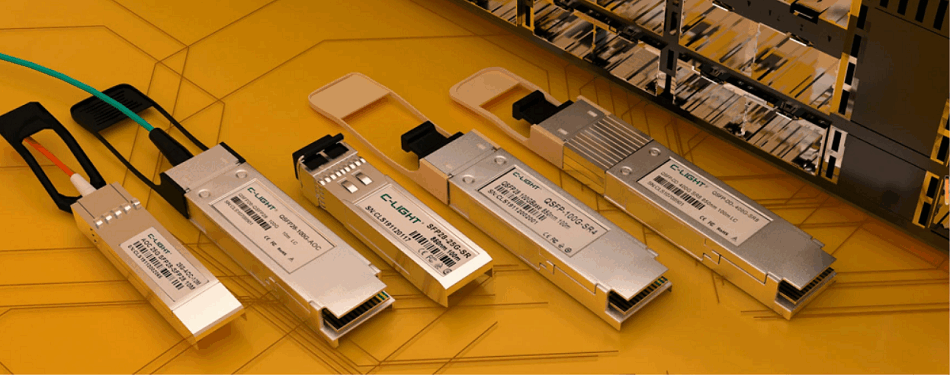
C-LIGHT 1.6T OSFP-RHS optical transceiver is a high-performance transceiver for next-generation data centers, featuring OSFP packaging and 1.6Tbps transmission capability. Its RHS design enhances thermal management and space efficiency while maintaining compatibility with QSFP-DD interfaces. Targeting 800G/1.6T Ethernet, AI clusters, and hyperscale cloud infrastructures, it utilizes 8x200G PAM4 modulation with integrated DSP and forward error correction for signal integrity. The low-power architecture and hot-swappable functionality make it ideal for high-density, low-latency optical interconnects.

 TEL:+86 158 1857 3751
TEL:+86 158 1857 3751 
























































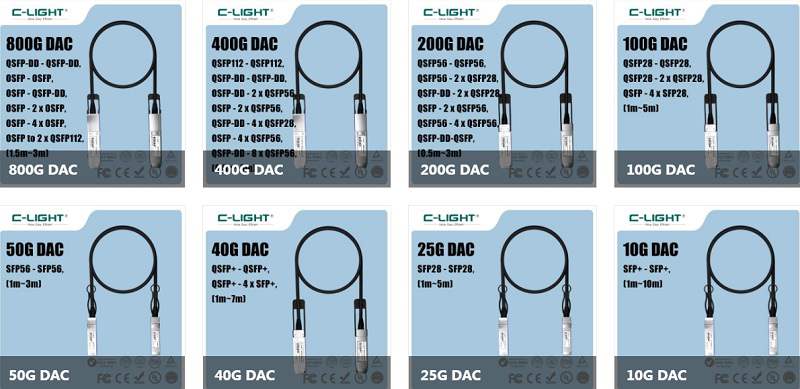

 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
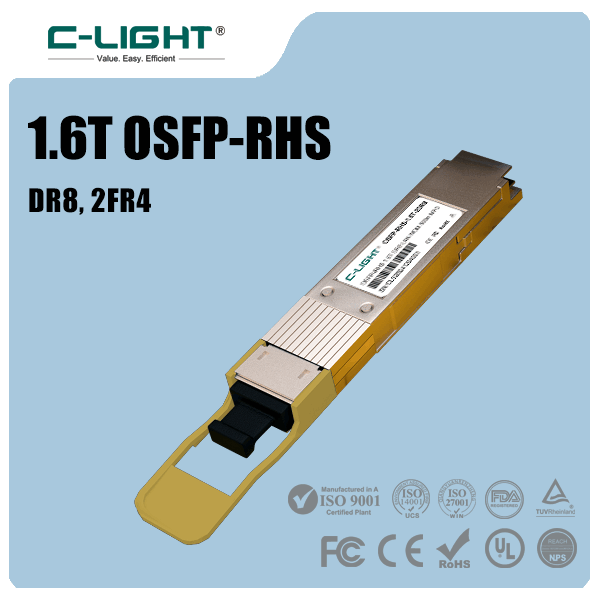 >
>
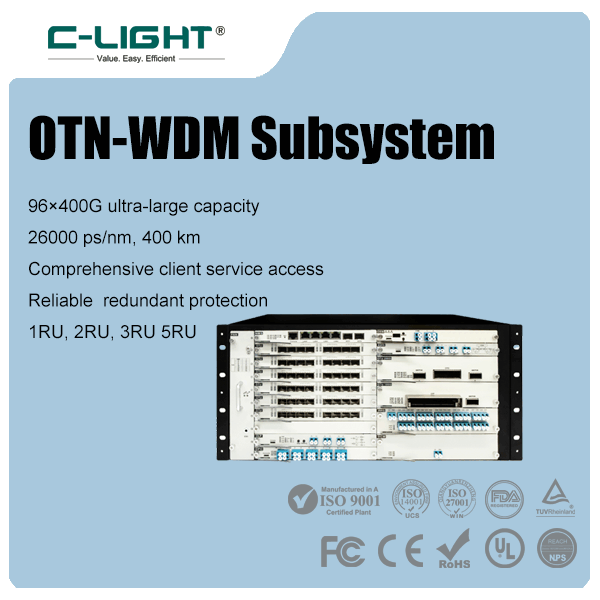 >
>
 >
>
