
In 2025, the forecast for the global AI market size has shifted from a technological topic to an economic issue. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, the global AI market is projected to reach $4.8 trillion by 2033, making it the most dominant frontier technology.
From "server rooms" to "smart factories," data centers are undergoing the most profound paradigm shift since the birth of the internet. This transformation is driven by the increasingly close logical relationship between AI technology and infrastructure, as well as the resulting reshaping of the global economic landscape.
01 Core Shift from Resource Hosting to Intelligent Generation
The historical role of data centers is being redefined. Traditionally, data centers have essentially served as "digital real estate," providing secure and stable environments to host clients' IT equipment. Key metrics for evaluating their value included the number of cabinets, power capacity, and network connectivity.
With the advent of the era of large models, AI workloads' demand for computing resources has grown exponentially, pushing traditional IDC models to their limits. In the era of large models, the traditional approach will lead to exponentially rising iteration costs, structurally constrained urban intelligent governance capabilities, and lagging industrial intelligence compared to the pace of global technological advancements.
The direct outcome of this shift is the rise of AI data centers. Unlike traditional IDCs, AIDCs are no longer mere collections of hardware but next-generation intelligent productivity infrastructures centered around AI tasks, redefining computing, networking, energy efficiency, scheduling, and operational models.
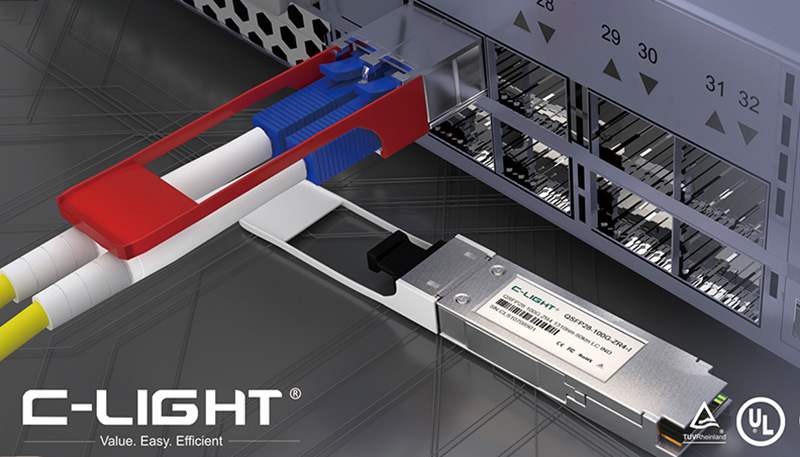
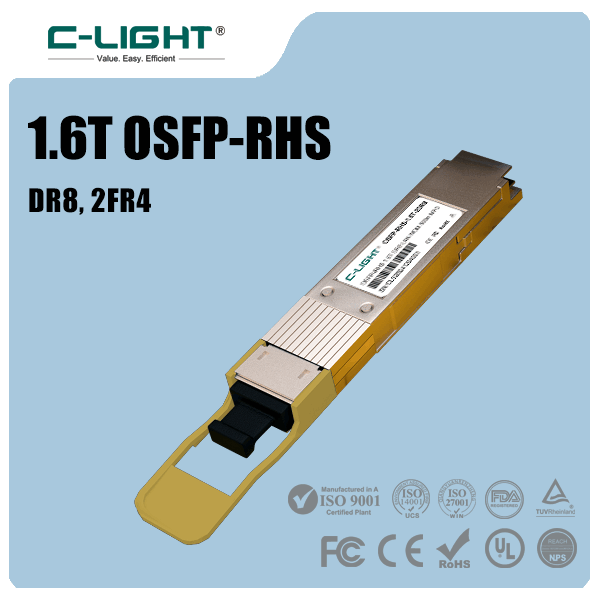
The 1.6T OSFP-RHS, utilizing advanced technologies such as 3nm DSP chips, achieves lower power consumption compared to standard modules. Its compact size allows for the deployment of more optical module ports on switch front panels, thereby increasing total bandwidth capacity. This makes it particularly suitable for AI computing centers, which are highly sensitive to power consumption and heat dissipation while requiring high bandwidth density.
The 1.6T OSFP-RHS is a cutting-edge product designed to address the explosive growth in AI computing power, with its core advantages lying in higher energy efficiency and port density.
02 AI Demand Drives Fundamental Restructuring of Data Center Architecture
The advancement of AI and the development of data centers have become tightly coupled technologically. AI's insatiable demand for computing resources is driving changes in infrastructure.
This transformation is first reflected in the "moon-shot" increase in computing density. NVIDIA's Blackwell Ultra, set for mass production by the end of 2025, will increase FP4 inference performance by 1.5 times, while the Vera Rubin platform, expected in 2026, will further boost performance by 3.3 times. This will push single-cabinet power to an astonishing 600kW.
Faced with such high heat density, traditional air cooling is no longer sufficient, leading to the widespread adoption of liquid cooling solutions at the cabinet, board, and even wafer levels. Microsoft's microfluidic channel technology can reduce GPU temperatures by 65%, delivering a threefold improvement in energy efficiency for data centers.
AI also imposes higher demands on data center network architectures. Large model training generates up to 30% intra-machine All-Reduce traffic, driving switch chips into the 51.2T era. Co-packaged optics technology shortens SerDes to 5mm, reducing power consumption by 40% and laying the foundation for "GPU pooling."
The challenges of power and cooling are equally daunting. For AI workloads, a reduction of 0.1 in PUE can save up to 32 million RMB annually for a 10,000-card cluster. More notably, green operations have become a source of profitability—12% of the EBIT for some AIDCs already comes directly from "zero-carbon operations."
03 Industrial Shift from Hardware Leasing to Value Co-Creation
The deep integration of AI and data centers is giving rise to new business models and industrial ecosystems. The traditional "cabinet leasing" model is being replaced by more profound value co-creation models.
A "three-stage leap" in business models clearly illustrates this transformation trajectory:
The first leap is from IaaS to MLaaS, where customers no longer lease physical hardware but directly subscribe to "computing power packages."
The second leap is from MLaaS to DaaS, where operators turn desensitized industry data into "ready-to-use datasets."
The third leap is the more radical Outcome-as-a-Service model, where operators and customers sign "performance-based agreements" and share revenue based on business outcomes.
This shift has also led to further specialization within the data center industry. According to an analysis by the China Industrial News, the industry has evolved into a four-layer stack:
Computing infrastructure providers focus on construction and energy management.
Intelligent platform providers offer full-stack software, from bare metal to large model scheduling.
Data service providers specialize in data cleaning, labeling, and compliance.
Industry solution providers act as "AI partners," delivering end-to-end solutions for clients.
The value of AI data centers is no longer confined to the technological realm but also extends to their role in boosting regional economies. For example, according to the Atlanta Chamber of Commerce, the AI data center built by Microsoft in Atlanta is estimated to generate over $2 billion in economic benefits annually for the state of Georgia, creating thousands of jobs.
04 Global Landscape: Strategic Competition Between Nations and Enterprises in the Computing Era
Globally, competition in AI data centers has risen to the level of national strategy. This competition is reflected not only in technical capabilities but also in ecosystem development and growth models.
U.S. tech giants are building computing ecosystems through deep integration of capital and technology. NVIDIA and OpenAI's partnership plans to deploy 4 to 5 million GPUs, equivalent to twice NVIDIA's annual shipments, a strategic move seen by industry insiders as "capital for ecosystem lock-in."
China has adopted a different development path. Through the "East Data, West Computing" project, cross-regional computing power scheduling efficiency has increased by 40%. The Wuhu Digital Island uses liquid cooling technology to reduce PUE to 1.09, showcasing the unique advantages of distributed architectures. In 2025, China's intelligent computing power reached 18 EFLOPS, a tenfold increase from three years ago.
Europe is also actively investing in AI infrastructure. The AI data center jointly built by NVIDIA and Deutsche Telekom in Munich, equipped with 10,000 NVIDIA hardware units, represents a multi-billion-euro investment aimed at creating the world's first industrial AI cloud platform.
This evolution in the global landscape is reflected not only in geographical distribution but also in the allocation of value across the industry chain. Technological blockades and independent innovation are fueling intense competition worldwide. The three-tier AI chip control system implemented by the U.S. in 2025 aims to maintain a 12-month technological lead.
05 Future Outlook: Green, Collaborative, and Autonomous AI Infrastructure Networks
Looking ahead, the collaborative development of AI and data centers will exhibit three major trends: greening, collaboration, and autonomy.
Microsoft's Fairwater AI data centers are directly interconnected via dedicated networks, enabling rapid data flow between data centers and allowing facilities in different states to work together as an "AI super factory."
Autonomous operation and maintenance will become a core competency for future data centers. AI digital employees will provide 7×24 monitoring, with fault prediction accuracy exceeding 99.5%, reducing on-site maintenance personnel by 80%. Such autonomous intelligent management will not only lower operational costs but also maximize computing power utilization through precise resource scheduling.
While companies are grappling with cooling technologies for AI data centers, Google's Willow quantum chip has already achieved a 13,000-fold advantage in specific algorithms, making "quantum-classical hybrid computing" a new standard for supercomputing centers.
This technological leap suggests that the "smart factories" we see today are merely an intermediate stage in the evolution of AI infrastructure.
U.S. tech giants are building computing empires through capital and ecosystem integration, while China is exploring distributed collaborative paths through institutional innovation.
When NVIDIA became the world's first company with a market capitalization of $5 trillion, the market provided a clear answer. In the future, the most powerful intelligence may no longer reside in isolated data centers but flow through a globally connected green computing network, becoming a new foundation driving the progress of civilization.
 TEL:+86 158 1857 3751
TEL:+86 158 1857 3751 


























































 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
