Amid the global wave of digital transformation, the rapid development of artificial intelligence is fueling an explosive growth in computing power demand. Predictions indicate that global AI computing power demand will increase more than tenfold within the next 3 years.
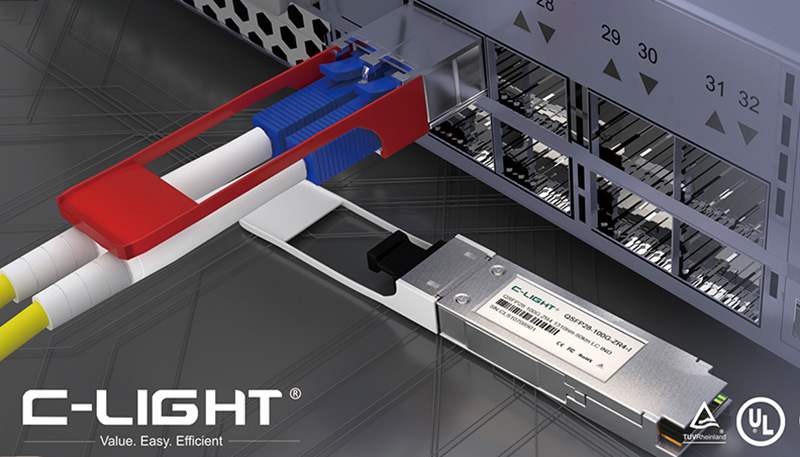
As the core component in data centers and communication networks responsible for photoelectric conversion, optical transceivers directly impact the speed and efficiency of data transmission. They act as the "information highways" of the computing power network, entering a golden age propelled by the AI computing boom.
01 Market Boom: Demand-Driven High-Speed Growth
The significant increase in capital expenditure by cloud service providers confirms the industry's high growth trajectory.
Google raised its 2025 capital expenditure guidance from $75 billion to $85 billion, primarily for AI infrastructure and server investments. Meta also increased its 2025 capital expenditure guidance from $64 billion to $72 billion, focusing heavily on AI data centers.
This growth stems from AI computing power having formed a complete closed-loop, from infrastructure investment to commercial application.
Overseas cloud providers not only possess globally leading AI infrastructure but have also built a comprehensive ecosystem spanning chips, frameworks, models, and applications. Overseas AI infrastructure construction is transitioning from an "investment phase" to a "harvest phase," establishing a virtuous cycle of "computing investment → commercial monetization → reinvestment."
Consequently, the demand for optical transceivers continues to maintain high growth rates. In 2024, deployments of 400G and higher-speed optical transceivers increased by 250% year-on-year, with projections suggesting over 50% year-on-year growth in 2025.

02 Technology Evolution: Higher Speeds and New Breakthroughs
Currently, optical transceiver technology is rapidly evolving along two dimensions: increased speeds and new technological breakthroughs.
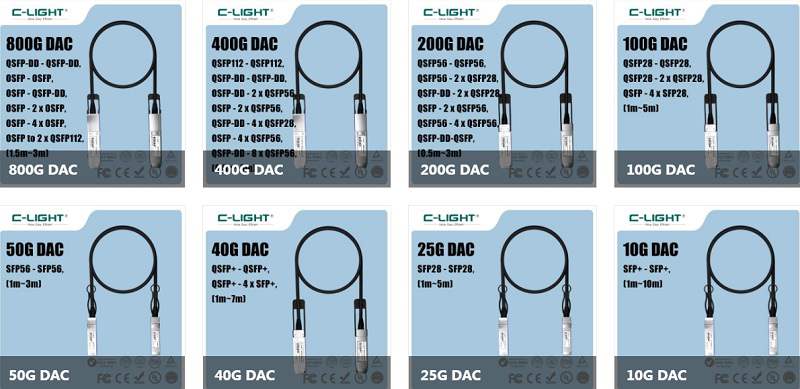
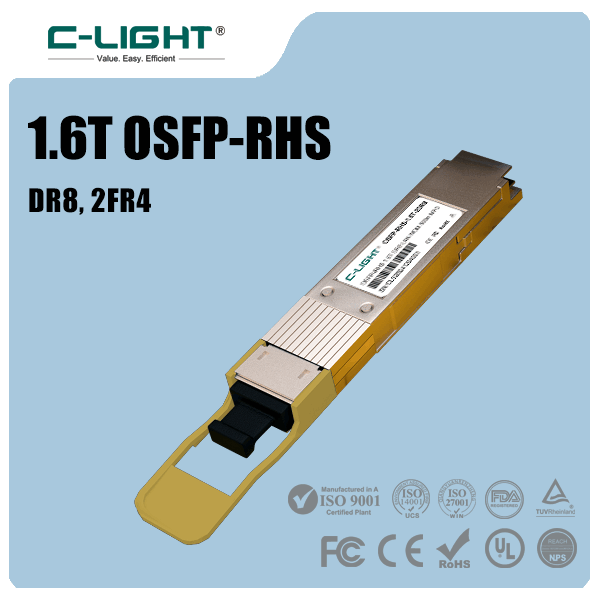
In terms of speed, 400G has become the mainstream solution in global data centers. 800G entered large-scale commercial deployment in 2024 and is expected to become mainstream in 2025. 1.6T optical transceivers, representing the direction for the next 2-3 years, are already being strategically deployed.
More notably, shipments of 800G optical transceivers in 2025 are projected to grow 100% year-on-year. 1.6T modules will begin shipping, with 3.2T expected to start entering the market around 2029.
The ratio of optical transceivers paired with new-generation AI chips has increased from approximately 1:3 to 1:4.5, and even reaches 1:8 in specific ASIC training clusters. For every high-end AI chip sold, a greater number of high-speed optical transceivers is required.
Regarding new technologies, Silicon Photonics is accelerating its adoption, offering significant advantages of 40% lower power consumption and 20% cost reduction. The Linear-drive Pluggable (LPO) approach, which removes the DSP chip, notably reduces power consumption and latency.
Co-packaged Optics (CPO) represents a more advanced direction, expected to enter large-scale deployment around 2026-2027, paving the way for future 3.2T/6.4T speeds.
03 Future Trends: Global Competition and Market Outlook
The optical transceiver industry has transformed from a cyclical growth sector into a strategic field characterized by "cross-cycle high growth" attributes.
Goldman Sachs has raised its 2026 demand forecast for 800G optical transceivers to 33.5 million units, a 58% increase from its previous prediction. Demand for 1.6T modules in 2026 is projected to reach 7 million units.
The total global market value is also showing rapid growth, expected to reach $12.73 billion in 2025 (a 60% year-on-year increase) and $19.37 billion in 2026 (a 52% year-on-year increase).
Regarding the geographical competitive landscape, the procurement share of Ethernet/DWDM optical transceivers by the five major US cloud giants (Amazon, Google, Meta, Microsoft, Oracle), after over a decade of steady growth, is projected to gradually decline.
While their spending on optical transceivers continues to grow, the rate of increase is ultimately expected to lag behind the rest of the global market.
Concurrently, Chinese companies are significantly increasing their optical component budgets and are well-prepared—potentially able to circumvent US tariffs through alternative supply chains if necessary.
This shift also reflects how the global AI race is accelerating digital transformation across industries, leading to explosive growth in cloud services like video AI model training and inference.
 TEL:+86 158 1857 3751
TEL:+86 158 1857 3751 

























































 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
