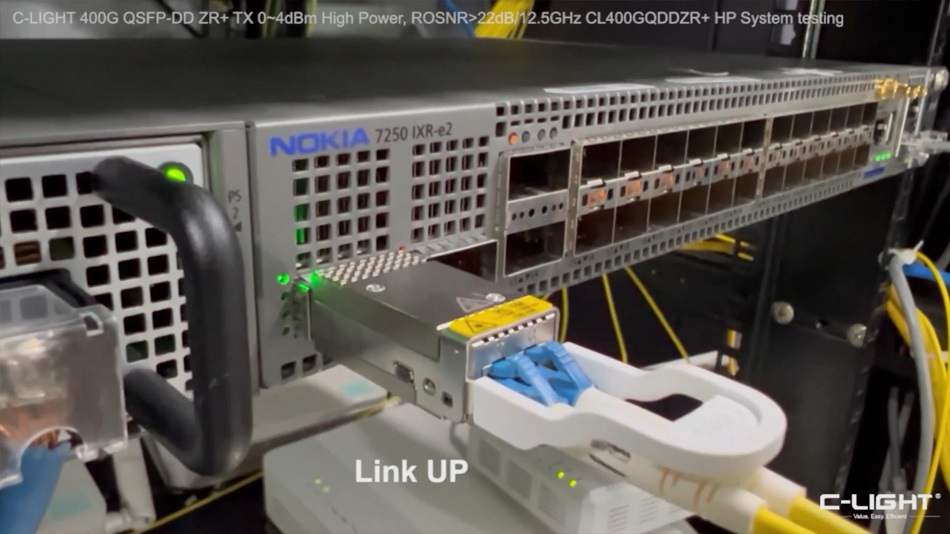

Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is an optical fiber communication technology that significantly enhances transmission capacity by multiplexing optical signals of different wavelengths into a single fiber for data transmission. This technology has become fundamental to modern communication backbone networks. The emergence and development of DWDM technology primarily stem from the explosive growth in bandwidth demand driven by internet services and the limitations posed by electronic bottlenecks in traditional Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) systems.
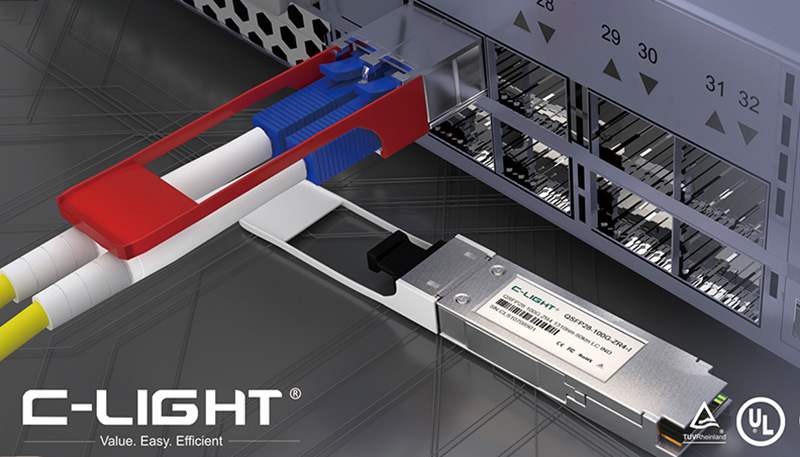
The basic principle of DWDM technology involves utilizing the broadband resources of single-mode fibers in the low-loss 1.55μm wavelength region. The low-loss spectrum of the fiber is divided into multiple optical channels, each carrying a dedicated wavelength. At the transmitting end, a multiplexer combines these signals, which are then transmitted through a single fiber. At the receiving end, a demultiplexer separates the signals back into their individual wavelengths. This process can be likened to merging multiple highway lanes into one super-wide lane and then separating them back into individual lanes at the destination. Commercially available DWDM systems can now achieve transmission capacities of up to 160 wavelengths per fiber, with continuous improvements driven by technological advancements.
Compared to traditional single-channel systems, DWDM technology offers several significant advantages. First, it dramatically increases the communication capacity of network systems by fully leveraging the bandwidth potential of optical fibers. Second, DWDM systems are protocol- and transmission rate-agnostic, enabling simultaneous support for multiple protocols such as IP, ATM, SONET/SDH, and Ethernet, while handling data rates ranging from 100 Mb/s to 2.5 Gb/s and beyond. Additionally, DWDM systems are known for their ease of capacity expansion and high reliability. Their ability to directly support multiple services makes them highly promising for modern communication networks.
The architecture of a DWDM network consists of several key components and node types, forming a comprehensive optical transmission network. Understanding these architectural elements is essential for mastering DWDM technology.
 TEL:+86 158 1857 3751
TEL:+86 158 1857 3751 
























































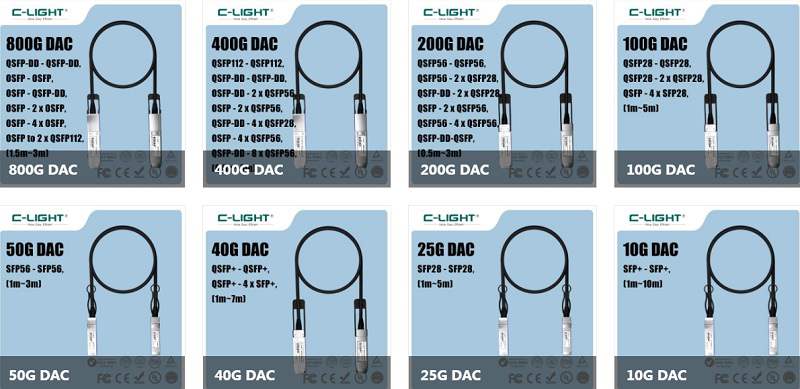

 >
>
 >
>
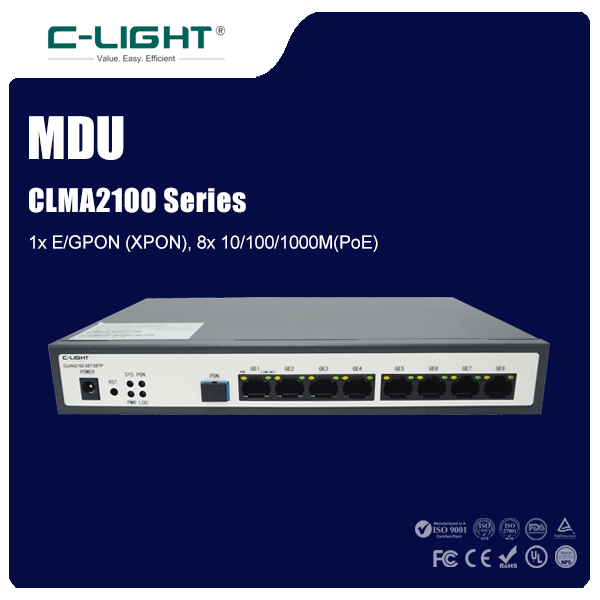 >
>
 >
>
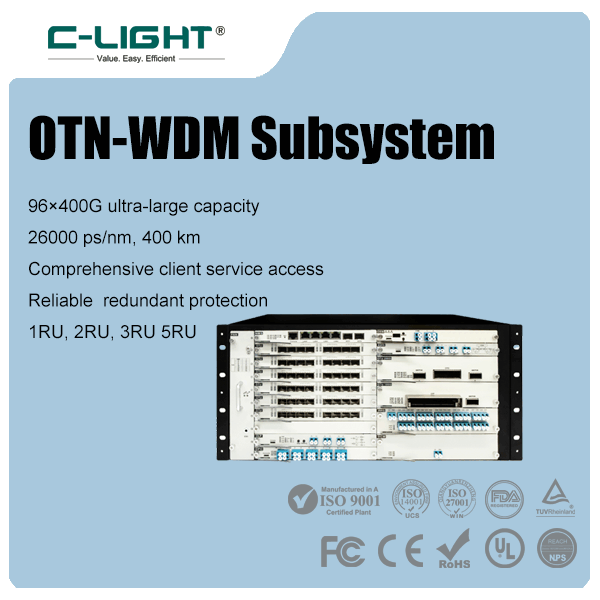 >
>
 >
>
